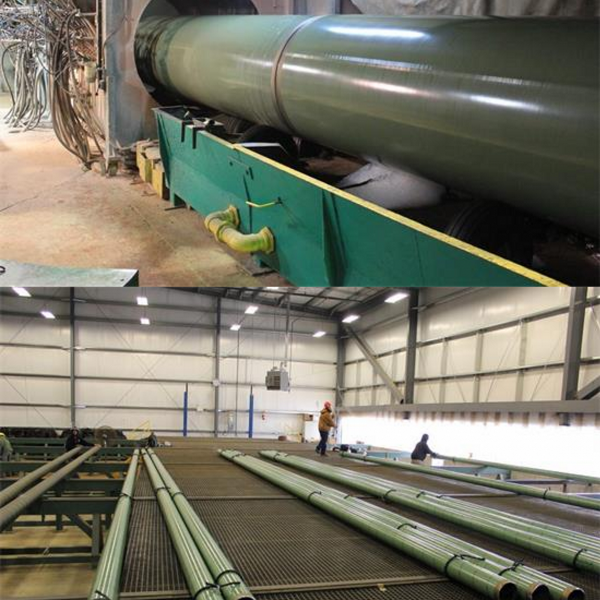
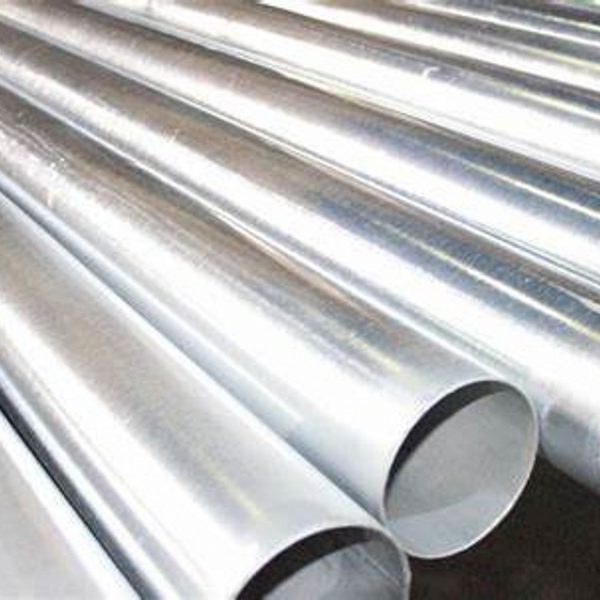
Stainless Steel Perforated Tube
Holic® offers Stainless Steel Perforated tube. Hole patterns available for Stainless steel perforated tube/pipes include round, square, hexagonal, oval and special openings.
Stainless Perforated metal sheets can be processed various of types and applications products, such as perforated metal tube, perforated metal pipe filter.
Item Name: Stainless Steel Perforated Tube.
Brand: HOLIC®.
Product Description
Stainless Steel Perforated Tube
Holic® offers Stainless Steel Perforated Tube. Hole patterns available for Stainless steel perforated tube/pipes include round, square, hexagonal, oval and special openings.
Stainless Perforated metal sheets can be processed various of types and applications products, such as perforated metal tube, perforated metal pipe filter.
Item Name: Stainless Steel Perforated Tube.
Brand: HOLIC®.
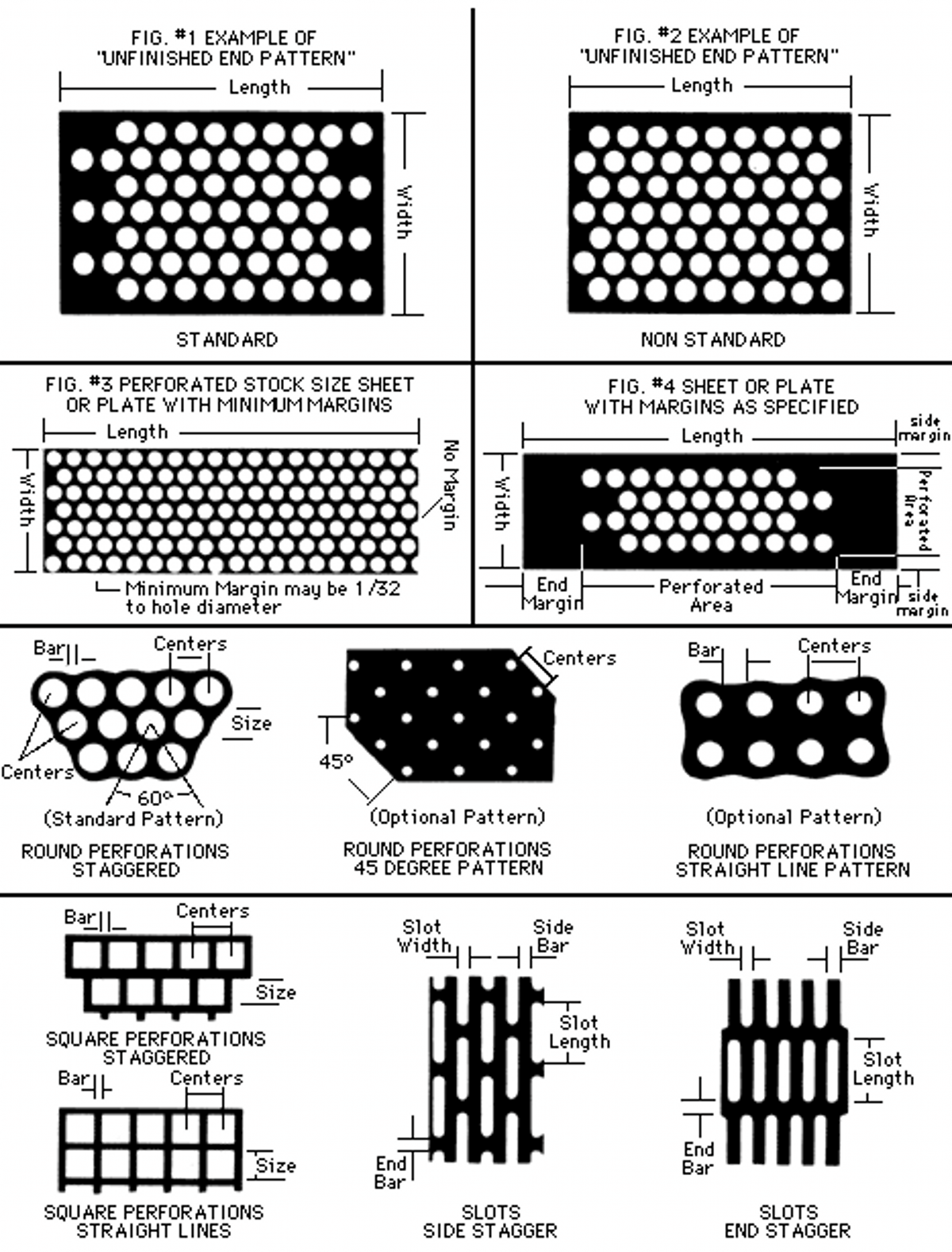
Perforated Patterns
The majority of the patterns shown within each section represent the most commonly used patterns that our existing tooling produces. Due to the versatility of the tools and presses, it is not practical to show every possible pattern that can be produced. Because of the vast number of patterns that can be produced from our tools, it is likely that your requirement can be fulfilled with existing tooling.
In the event we can not produce a pattern with existing tooling, the Customer Service Representative will either quote the closest alternate and/or obtain the price to have our on-site tool and die shop build a proprietary tool.
Holic® Supply Range:
The mostly used stainless steel perforated tubes include 304, 304L, 316, 316L. Carbon steel can also be used.
Perforated stainless steel tubing is made of either T304 stainless steel sheet or T316 stainless steel sheet that has been punched with a series of holes to give you a nominated pattern. The pattern can vary depending on the hole size, distance between holes and the thickness of the material.
Perforated stainless steel tubes has many various uses, including catering for the architectural, chemical, mining & refining, the uses are endless.
|
GAUGE |
HOLES |
CENTERS |
OPEN AREA % |
| 30 | .020″ | .045″ |
20% |
| 26 | 1/32″ | 1/16″ |
22% |
| 26 | .033″ | .055″ STRAIGHT |
29% |
| 24 | 3/64″ | 3/32″ |
23% |
| 26 | .050″ | .066″ STRAIGHT |
52% |
| 26 | 050″ | 5/64″ |
37% |
| 22 | 1/16″ | 3/32″ |
40% |
| 22,26 | 1/16″ | 7/64″ |
30% |
| 20,18 | 1/16″ | 1/8″ |
23% |
| 22,20 | 5/64 | 1/8″ |
35% |
| 20,18,16 | 3/32 | 5/32″ |
33% |
| 22 | .117 | 5/32″ |
51% |
| 26-11 | 1/8 | 3/16″ |
40% |
| 20-16 | 5/32″ | 3/16″ |
63% |
| 24-14 | 3/16″ | 1/4″ |
51% |
| 18,11 | 3/16″ | 5/16″ |
33% |
| 22-16 | 1/4″ | 5/16″ |
58% |
| 20-14,11 | 1/4″ | 3/8″ |
40% |
| 10 | 3/8″ | 1/2″ |
51% |
| 18,16,11 | 3/8″ | 9/16″ |
40% |
| 20,16,14,11 | 1/2″ | 11/16″ |
48% |
| 11 | 3/4″ | 1″ |
51% |
The thickness of metal tubes perforated: 0.2mm to 15mm
Opening diameter: 0.2mm to 100mm
Stainless Steel, unlike carbon steel, is corrosion resistant. It contains chromium which, when exposed to oxygen, creates an invisible protective film. Stainless steel types are classified into three different groups based on their ability to be hardened. Austenitic stainless steels, which can be hardened by cold working, meet a wide range of design criteria. They are essentially non-magnetic, although they may become slightly magnetic due to cold working.
Stainless steel perfororated tubes are straight-chromium types that can be hardened by heat treatment.
Commonly Perforated Stainless Steel Types
304 (Austenitic)
One of the most widely used general-purpose stainless steels. It possesses an excellent combination of strength, corrosion resistance and fabricates well. To reduce carbide precipitation when welding, use 304L for its lower-carbon content.
316 (Austenitic)
Superior corrosion resistance compared to other 300 series alloys when used in used harsh corrosive environments (ex. sea water, chemicals, etc.). To reduce carbide precipitation when welding, use 316L for its lower-carbon content.
321 (Austenitic)
Titanium stabilized stainless steel to prevent intergranular formation of chromium carbide. It exhibits strength characteristics superior to those of 304 stainless, thus making it best suited for parts which cannot be subsequently annealed.
410 (Martensitic)
The lowest alloy content of the three general-purpose types. It is a heat-treatable chromium type used for highly stressed parts needing the combination of strength and corrosion resistance.
409 (Ferritic)
The lowest chromium content of the stainless steels, 409 combines good elevated temperature corrosion resistance with medium strength, good formability, and overall cost.
430 (Ferritic)
A general-purpose non-heat-treatable chromium type used for highly polished trim applications in mild atmospheres. Its strengths are in ductility, formability, good corrosion and oxidation resistance, thermal conductivity and finish quality.
| Stainless Steel | Lbs. Per Square Foot | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge | Mean of Gauge | Min. of Gauge | Max. of Gauge | 300 Series | 400 Series |
| 7 | .1875 | .1735 | .2015 | 7.871 | 7.70 |
| 8 | .1650 | .1510 | .1790 | 6.930 | 6.78 |
| 9 | .150 | .136 | .164 | 6.300 | 6.165 |
| 10 | .135 | .129 | .141 | 5.670 | 5.562 |
| 11 | .120 | .115 | .125 | 5.040 | 4.944 |
| 12 | .1054 | .1004 | .1104 | 4.427 | 4.342 |
| 13 | .090 | .0860 | .094 | 3.780 | 3.708 |
| 14 | .0751 | .0711 | .0791 | 3.154 | 3.094 |
| 15 | .0673 | .0643 | .0703 | 2.826 | 2.766 |
| 16 | .0595 | .0565 | .0625 | 2.499 | 2.451 |
| 17 | .0538 | .0508 | .0568 | 2.259 | 2.211 |
| 18 | .048 | .045 | .051 | 2.016 | 1.978 |
| 19 | .042 | .039 | .045 | 1.764 | 1.726 |
| 20 | .0355 | .0335 | .0375 | 1.491 | 1.463 |
| 21 | .0324 | .0304 | .0344 | 1.360 | 1.33 |
| 22 | .0293 | .0273 | .0313 | 1.231 | 1.207 |
| 23 | .0264 | .0249 | .0279 | 1.1088 | 1.085 |
| 24 | .0235 | .0220 | .0250 | .987 | .968 |
| 25 | .0209 | .0194 | .0224 | .8778 | .8589 |
| 26 | .0178 | .0163 | .0193 | .748 | .7315 |
| 27 | .0165 | .0150 | .0180 | .693 | .6781 |
| 28 | .0151 | .0136 | .0166 | .634 | .6206 |
| 29 | .0138 | .0123 | .0153 | .5796 | .5671 |
| 30 | .0125 | .0110 | .0140 | .525 | .5137 |







